Understanding the Process Behind Sewage Treatment Plants
STPs or municipal sewage treatment facilities are vital in maintaining our population’s and environment’s well-being. These devices are designed to clean and treat wastewater before it returns to the environment. Proper wastewater treatment is also necessary in municipalities, where large amounts of sewage are produced daily to avoid water resource contamination, pollution, and wastage of potential opportunities for sustainable urban development. The blog narrates the history of STPs for municipalities in detail. It explains how they contribute to more effective water management thereby linking the entire procedure to Sarvo Water, which runs these vital biological engines.

What is a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)?
An STP, or sewage treatment plant, is an organization that collects and treats waste from residential, industrial, and commercial sites. An STP removes pollutants from sewage to ensure that the water returned to a natural body, such as a river, lake, or ocean, is safe for human health and the environment. Moreover, after treatment, this water can be reused for industrial or agricultural purposes.
Massive volumes of sewage are generated in urban municipalities because of the high number of inhabitants, commercial enterprises, and industrial activities. For this reason, STPs play a pivotal role in waste handling in these cities, and the treatment process has to be reliable and scalable enough to meet increasing demands.
How Sewage Treatment Happens
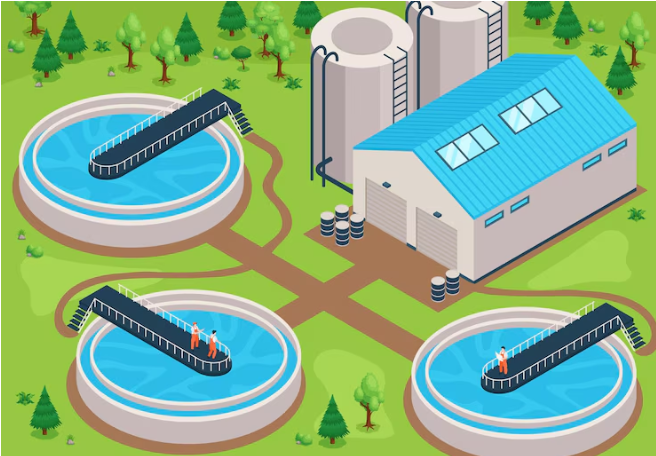
Solids, organic material, harmful microbes, and hazardous chemicals are removed from wastewater through various processes called sewage treatment. It usually has three main steps: primary, secondary, and tertiary treatment.
- Primary Treatment
The primary treatment of sewage deals with removing large solid particles. Raw sewage is taken to a Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) where it gets filtered to remove debris like paper, plastics, and trash. Wastewater undergoes processing in main sedimentation or clarifying tanks that separate lighter substances from heavier solids. Pathogens, fine particles, and dissolved organic debris require further treatment.
- Secondary Treatment
Biological processes are applied during the secondary treatment of sewage to remove unwanted bacteria, nutrients, and organic materials. The aerobic treatment provides for the oxidation of pollutants into carbon dioxide, water, and biomass by supplying air to a tank with wastewater and microorganisms. Since they are made from porous materials, trickling filters encourage the proliferation of microorganisms and reduce hazardous pathogens, suspended particulates, and biological oxygen demand. However, some nutrient loads may persist for a while, thus causing eutrophication.
- Tertiary Treatment
The aim of the tertiary treatment is the purification of water through the removal of the remaining pollutants, including nutrients, suspended small particulates, and pathogens. Among some of the possible processes in this stage are filtration, chemical treatment, UV or chlorination disinfection, or biological or chemical nutrient removal. The water should be further filtered and disinfected after treatment so that it becomes potable, and normally, it is safe for reuse or disposal.
Role of Sarvo Water in Sewage Treatment
Sarvo Water is especially focused on water treatment solutions, mainly through the design, installation, and operation of Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs), based on its technological innovation. More than ever before, efficient sewage treatment is required due to the growing urban areas and population. Sarvo Water helps the towns by providing ecologically sustainable and energy-efficient bespoke solutions.
- Bespoke Solutions
Sarvo Water designs STPs based on the specific needs of the municipality. Every municipality is unique in meeting its specific needs and sizes based on population, industry operation, and geographical location. Such factors each play a vital role in terms of designing cost-effective, scalable, and efficient STPs by Sarvo Water’s engineers. During the treatment process, both ecological requirements and local rules should be adhered to.
- Advanced Technologies
Utilizing the latest technological advancement, Sarvo Water is treating sewage in the most effective manner and sustainability. To deliver high-quality treated water, their high-tech solutions employ novel techniques such as membrane bioreactors moving bed biofilm reactors and sophisticated filtration techniques.
Fourth, Sarvo Water equips its STPs with smart technology and automation, allowing for the facility to be managed through remote modes and monitored in real time. Predictive maintenance can also be undertaken to allow the facility to function at an optimum level and reduce costs further.
- Sustainability and Reuse
To do this, Sarvo Water also focuses on resource recovery and water reuse so that treated wastewater can be returned to its environment for non-potable uses like industrial cooling, park, and garden irrigation, or even toilet flushing in municipalities classified as water-scarce. Efficient sewage treatment by Sarvo Water helps conserve precious freshwater resources while lessening the detrimental effects of wastewater.
Conclusion
Sewage treatment plants form the basis of environmental and public health protection, especially within cities with growing populations. The three main stages of wastewater treatment, which include primary, secondary, and tertiary, have been designed to remove the three different types of contaminants separately. The innovative and eco-friendly STP solutions offered by Sarvo Water help communities overcome all these challenges. Sarvo Water enhances wastewater management by adopting cutting-edge technologies and emphasizing water reuse, helping to create a more resilient and sustainable future for metropolitan communities.