Explore the World of Sewage Management: Methods, Importance, and Disposal
Discover the importance of sewage management methods, including treatment and disposal, to protect the environment and human health.
Introduction to Swage Management
Sewage management is the process that disposes of waste for human benefit. Sewage treatment involves three Distinct processes: treatment, filtering, and receiving sewage. This also includes getting rid of sewage in a way that does not threaten the environment or harm people’s health.
This article will provide you with a basic understanding of sewage management and the reasons behind its implementation sewage management.
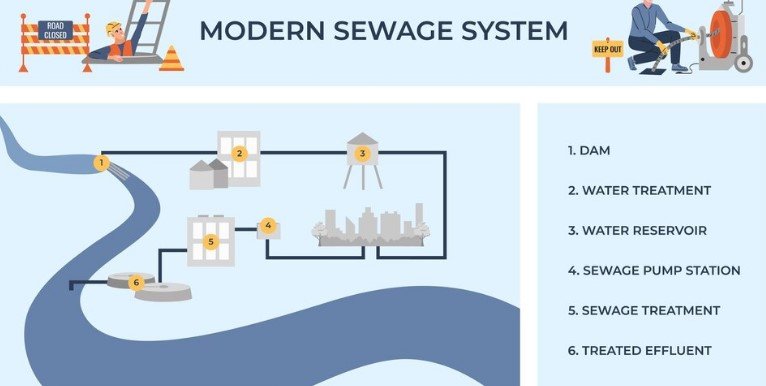
Sawage Management Methods
The Creation of waste is one of the most inevitable and natural aspects of human existence. Water is essential for human existence to fulfill many functions. These life processes include domestic labor, industrial production, and services such as restaurant establishments and railroads.
Each of these uses generates large amounts of wastewater. Despite annual replenishment, natural water reserves are a limited resource.
We are completely dependent on water and other natural resources, and as the human population increases daily, the need for water for various domestic purposes also increases.
Therefore, to conserve this water for future generations, you must reuse the water you waste. Otherwise, the resources will not be replenished until our descendants arrive.
Because it is essential for the present and future generations, we use these sewage management techniques to recycle spent waste water to maintain our environment.
If this mismanagement of water supply continues then adverse situations like shortage or drought are certain to occur in the future.
To prevent this type of contamination you must be knowledgeable about organized sewage treatment techniques. This post will provide you with some basic knowledge of sewage management to help prevent environmental and water pollution.
Definition of Sewage Treatment
Sewage treatment refers to a method of purifying industrial and domestic wastewater of pollutants. Physical, biological, chemical, and sludge water treatment are the four main technologies used to treat sewage water.
Using these technologies, wastewater is cleaned of all sewage components and turned into treated water that is safe for the environment and human use.
Learning fundamental sewage treatment techniques
Physical Method: It mainly involves using two processes, sedimentation, and filtration, to remove large and small floating and suspended solids from sewage.
Filtration is the first step to remove floating or suspended particles. Large open tanks are used to store the filtration after the suspended pollutants have had time to settle.
Biological Method: This process treats human waste and other degradable wastes using bacteria and microorganisms that convert sewage waste into byproducts such as sludge.
Chemical Method: In this process, chemicals are used to treat wastewater. To ensure that no infection spreads through waste water, chemicals are used to disinfect it.
Activated Sludge Method: In activated sludge technology, microorganisms consume organic matter in the effluent. The result of this operation is a cleaned effluent. To meet the oxygen requirement of the bacteria, a lot of air is introduced into this solution.
Before contaminated water enters natural water bodies, including lakes, rivers, oceans, and estuaries, the confinement removal process is completed.
Since pure water is difficult to find, the only factors that differentiate clean water from contaminated water are the concentration of impurities and the intended use.
Stated differently, water is considered contaminated if it is unsuitable for a particular use, such as swimming, fishing, drinking, etc. The main cause of water pollution is the leakage of impure wastewater into the surface or groundwater.
Additionally, various sewage management techniques can reduce the risk of water pollution to a great extent. Furthermore, non-polluted or safe drinking water is defined as water that is suitable for swimming, fishing, and other domestic uses other than drinking.
However, before talking about these technologies you should be aware of the main pollutants and forms of sewage.
Typically, three types of sewage are there-
Domestic Sewage
Used water from houses or apartments is included in the category of domestic wastewater. Sanitary sewage is another name for this type of waste.
It could also be water dripping from the shower or human feces. Our homes produce this wastewater every day as a result of regular household activities.
Industrial Wastewater
Contaminated water from manufacturing or chemical operations ends up in industrial wastewater. This sewage can contain many types of harmful substances. This waste can be hazardous and contain heavy metals because it is mainly produced by industries.
Storm Sewage
Stormwater is the term used to describe sewage runoff that collects in open channels as water particles from the atmosphere. This may apply to snowfall, drizzle, or rain. More than 99.9% of total wastewater is composed of household waste.
Domestic wastewater contains dangerous bacteria, although the main contaminants are defined as organic debris and plant nutrients. Nutrients that can be recovered during sewage treatment are present in this wastewater.
Disposal Methods of Sewage
The fundamental element of a sewage management system is sewage disposal technology. Disposing of the wastewater generated from homes, businesses, etc.
Contributes to the cleanliness of the environment. Popular techniques of sewage disposal used around the world are listed below.
Sewage Management Methods
Municipality Systems
A treatment facility is connected to the wastewater source in a municipal wastewater system. This facility effectively eliminates approximately 95% of the contaminants from used water.
To guarantee that this water is safe to use, the sludge is once again treated using anaerobic technology.
Off-Site Sewage System
One consequence of increasing urbanization is off-site sewage systems. In cities, homes are built on lots, and each lot is wired to a wastewater system.
These wastewater pipes collect waste from various houses and direct it toward the neighborhood sewage treatment facility. After treatment, the excess water is sent to a nearby irrigation field or river.
Localized Waste Management Septic system is another term for an on-site sewage system. The component of this disposal system is a septic tank, which allows sewage to be treated, disposed of, and similarly sludged at the waste generation site.
During this process, the waste material is processed and disposed of naturally. The on-site system typically consists of a disposal area and a septic tank that is the soil absorption place.
The wastewater solution is transported to this leach field, where it will eventually be broken down by microorganisms. These sewage-disposal technologies are reliable, clean, cost-effective, and efficient.
Full Wastewater System
A complete wastewater disposal system collects and flows domestic sewage water through multiple sewer lines. During this process, all the solid waste passes through several macerators or sharp blades. To prepare solid waste for further processing, it helps to reduce its dimension.
Lagoons
Lagoons are large, open ponds suitable for collecting domestic waste. Innumerable bacteria in these pools of water break down the waste. Air and sunlight accelerate the breakdown process, acting as catalysts in the process. In addition, algae support the mechanism by which bacteria reproduce in waste. Due to the presence of algae, the color of these lagoons looks green.
Pit Latrines
Pit latrines are a centuries-old technique for disposing of excreta in human civilization. These days, you can find them in isolated areas with limited water supplies. This disposal system includes trench latrines, ventilated improved pits, and boreholes. Larger groups use shallow trench latrines for short periods before filling them almost completely with soil.
Methods of Sewage Collection
Typically, a sewage system is made up of several underground pipes that transport wastewater released by cities.
To move sewage from the collection point to discharge, collection systems are installed with pipelines, manhole drains, holding basins, catch basins, inlets, and pump stations. The main means of collecting sewage in metropolitan areas are pipe systems and related accessories.
Combined System
The same collection system collects storm and domestic wastewater. Generally, large-diameter pipelines or tunnels are used to construct this storage system.
However, during wet seasons, this system can sometimes break down as water treatment facilities cannot handle large amounts of storm sewage.
Separate System
Separate wastewater systems that carry storm and domestic wastewater separately are a relatively recent practice in communities. Open water bodies, such as rivers, are used to dispose of rainfall and surface runoff sewage.
Installing catch basins or smallholding basins will allow higher water flow during the rainy season. However, domestic wastewater is sent to a treatment facility.
You have gained an understanding of treatment, collection, and disposal processes through an in-depth examination of sewage treatment technologies.
For additional Chemistry chapters, you can also visit our online courses on the Vedantu website. You can now download our Vedantu App for additional information on sewage control technologies.
Vedantu will give you complete information about each chapter, which will improve your understanding and help you perform well in the exam.
Conclusion:
Sewage management is essential for maintaining the health of the environment and protecting human welfare. We can better understand the importance of proper treatment and disposal of wastewater by examining the technologies involved in sewage management.
It is imperative to implement systematic sewage treatment technologies to prevent water pollution and guarantee a sustainable future for future generations.



