Discover Zero Liquid Discharge Plants: Revolutionizing Wastewater Treatment
Discover the Future of Wastewater Treatment with Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Plants
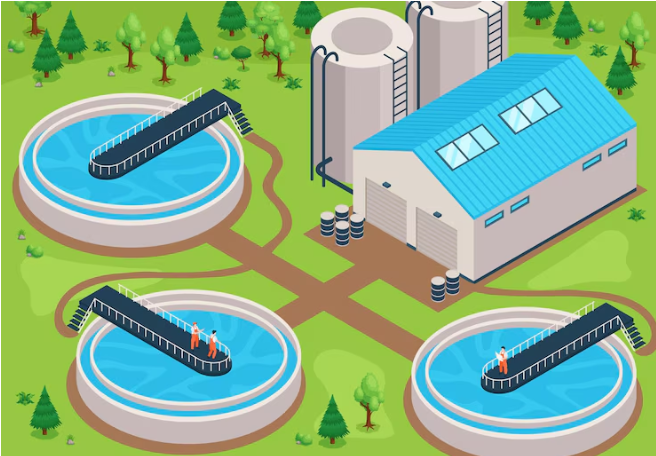
What is a Zero Liquid Discharge Plant?
Zero Liquid Discharge Plants (ZLD) There are state-of-the-art wastewater treatment systems that aim to remove liquid waste from industrial processes and leave little or no liquid waste.
Environmental Impact of Zero Liquid Discharge System
Zero Liquid Discharge System (ZLDS) requires careful planning and analysis before developing it. Since each site has a different combination of elements, there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach.
The ideal system is site-specific and takes into account the available footprint, operating expenses, various streams requiring treatment, wastewater composition and type, and other factors.
The following points should be considered when designing a system with zero liquid discharge.
Zero Liquid Discharge System (ZLDS) requires careful planning and analysis before developing it. Since each site has a different combination of elements, there is no “one-size-fits-all” approach.
The ideal system is site-specific and takes into account the available footprint, operating expenses, various streams requiring treatment, wastewater composition and type, and other factors.
The following points should be considered when designing a system with zero liquid discharge.
ZLD is a very effective wastewater treatment method, yet this technology has some unexpected side effects. In addition to using a lot of energy, the wastewater treatment process emits a lot of greenhouse gases (GHGs). When ZLD technology is powered by renewable energy sources, it can be particularly energy-efficient. Additionally, ZLD systems can work well in large-scale chemical manufacturing facilities.
Zero liquid discharge system should be achieved through pre-treatment, concentration, and heat treatment. Reverse osmosis and electrodialysis are two membrane technologies used to process wastewater in this process.
After the evaporation step, the dissolved solids precipitate as crystals, and they are removed from the stream using a filter press or centrifuge. Waste water utilization also includes the reuse of condensate water.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) System Applications
A Zero Liquid Discharge System A method that concentrates wastewater to the point of solubility, allowing the salts to be recovered and reused.
ZLD requires less complexity and capital than other systems. One advantage is that using less expensive alloys for the main process equipment reduces operating expenses. These are some of the benefits that come with this technology. They also make recycling and wastewater treatment more effective.
A Zero Liquid Discharge System is A method of extracting desirable solvents and water from wastewater. After the process, the remaining material is dehydrated to create pure water. Therefore, zero liquid outflow produces no waste.
Currently, fluids are essential for chemical and water operations. While most of this waste ends up in landfills, some of it can be recycled in whole or in part.
The power industry is increasingly using ZLDs due to tougher discharge standards. ZLD systems can also help remove toxins such as selenium and mercury down to parts per trillion.
This is particularly important for the power sector, whose processes require a lot of water. These factories need to find efficient ways to reuse their wastewater.
If these solutions can reduce these levels the energy and environmental costs of power plants will be reduced.
ZLD stands for Zero Liquid Discharge, an apparatus for treating and recycling wastewater in a closed-loop system.
The following are some typical ZLD system characteristics:
Pre-treatment: Pre-treatment, the initial stage of the ZLD system, is to clean the wastewater of particles and other impurities. Typically, a sedimentation tank, a filter, or a clarifier is used for this.
Evaporation: After pre-treatment, the wastewater is exposed to evaporation, which concentrates the remaining pollutants and removes water from the waste stream. Generally, a thermal evaporator or multi-effect evaporator is used for this.
Crystallization: Some ZLD systems crystallize the concentrated waste stream, which eliminates excess water and produces a solid waste product that can be disposed of or further treated.
Recycling: Reusing purified water from ZLD systems in industrial processes can help conserve fresh water supplies by reducing its demand.
Energy recovery: ZLD systems Often employ energy-intensive processes such as crystallization and evaporation. But these processes can also generate heat and other forms of energy that can be captured and reused, reducing the system’s overall energy use.
Monitoring and control: ZLD systems are Often equipped with control and monitoring systems that help maximize the system’s performance and guarantee that it is operating within design parameters.
These features allow ZLD systems to efficiently treat and reuse wastewater, which reduces freshwater demand, conserves water, and increases the general sustainability of industrial processes.
Zero Liquid Discharge Technology
The Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) The process is a relatively recent water treatment technology that generates electricity entirely from water. An alternative to traditional FGD treatment which is comparatively high-tech and capital-intensive, this technology is.
Nonetheless, some businesses have already switched to zero liquid production and are either selling or recycling the particles generated. For example, lithium can be extracted from cellars and brines found in American oil fields.
In contrast, gypsum can be extracted from mine water and flue gas desalination wastewater and sold for use in the production of drywall.
ZLD technology has various advantages
The first benefit is that it enables businesses to equip critical process machinery with less expensive alloys. Another benefit is that it makes waste disposal less expensive and enables businesses to recycle wastewater. Moreover, it has a strong potential to increase productivity. ZLD is increasing in popularity due to its various benefits. The cost of the ZLD system for your facility is partially determined by its zero liquid discharge system cost.
The volume of wastewater to be treated determines the ZLD cost. The total capital cost of the system may vary depending on its dimensions and characteristics.
If your waste stream is large enough then ZLD may not be a financially viable option. Thus, to build the ZLD facility, consider the following:
The price of the ZLD treatment system is an important consideration when making a purchasing decision. Whether or not you want to install an evaporation pond and how many components you need will determine the cost. ZLD systems can also be shipped to your location. However, freight charges may change depending on your location and time of year. If you want to reduce the cost of a zero liquid discharge system it may be worthwhile to install a membrane system.
FAQs about Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Plants
Q: What is a Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) plant?
A: A ZLD plant is an advanced wastewater treatment system that aims to eliminate liquid waste from industrial processes, leaving little to no liquid waste.
Q: How does a ZLD system work?
A: ZLD systems typically involve pre-treatment, concentration, and heat treatment. Membrane technologies like reverse osmosis and electrodialysis are used, followed by evaporation and crystallization to remove dissolved solids.
Q: What are the environmental benefits of ZLD systems?
A: ZLD systems can help reduce water pollution by effectively treating wastewater. When powered by renewable energy sources, they can be energy-efficient and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Q: What industries can benefit from ZLD technology?
A: Industries with high water consumption, such as power plants, chemical manufacturing facilities, and textile industries, can benefit from ZLD technology to manage their wastewater more sustainably.
Q: Are there any drawbacks to ZLD technology?
A: While ZLD technology is effective, it can be energy-intensive and emit greenhouse gases. However, these drawbacks can be mitigated by using renewable energy sources and optimizing system design.
Q: How can ZLD systems help with water conservation?
A: By treating and recycling wastewater, ZLD systems reduce the demand for freshwater, contributing to water conservation efforts in industries.
Q: What factors should be considered when designing a ZLD system?
A: Factors such as site-specific requirements, available footprint, operating expenses, wastewater composition, and type should be considered to design an efficient ZLD system.
Q: How can industries implement ZLD technology?
A: Industries can implement ZLD technology by conducting a thorough analysis of their wastewater treatment needs, designing a customized ZLD system, and ensuring proper maintenance and monitoring.



